Photovoltaic Spectral Responsivity and Efficiency under Different Aerosol Conditions

We assessed the impact of the variability of atmospheric composition on the spectral distribution of the incident solar spectral irradiance (SSI) and, therefore, its implication on various PV
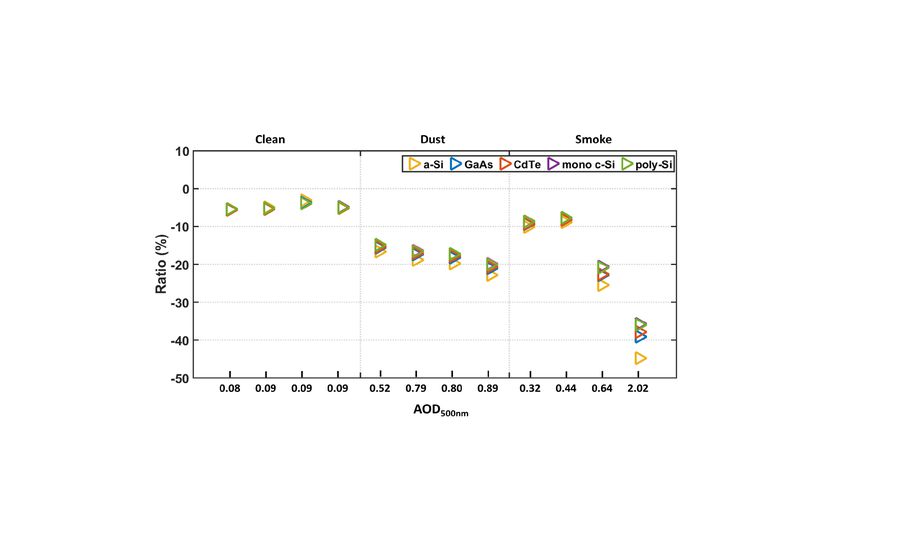
materials performance. Ground‐based measurements of global horizontal SSI have been conducted using a Precision Spectroradiometer (PSR) in the framework of the ASPIRE (Atmospheric parameters affecting SPectral solar IRradiance and solar Energy) project in Athens, Greece. The gathered data in combination with spectrally resolved radiative transfer under clear‐sky conditions contributed to the investigation of the atmospheric variables that attenuate irradiance (e.g., aerosols). In addition, since PV modules’ spectral absorptivity differs according to the semiconductor material used, the impact of the above‐mentioned spectral features on PV performance has been investigated in order to estimate the spectral impact between the theoretical and outdoor conditions on the yield of different PV technologies.
Overall, the results denote that smoke has a more significant effect than dust, while the effect on various technologies varies. The highest deviation compared to the STC was observed in the case of a‐Si.
Read the full article:
Kouklaki, D.; Kazadzis, S.; Raptis, I.‐P.; Papachristopoulou, K.; Fountoulakis, I.; Eleftheratos, K. Photovoltaic Spectral Responsivity and Efficiency under Different Aerosol Conditions. Energies 2023, 16, 6644. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16186644 .